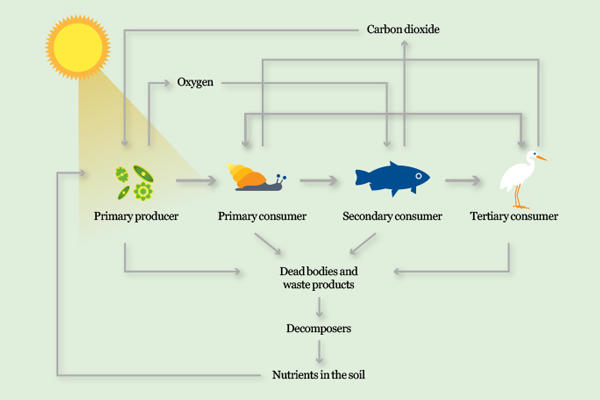
Food chain
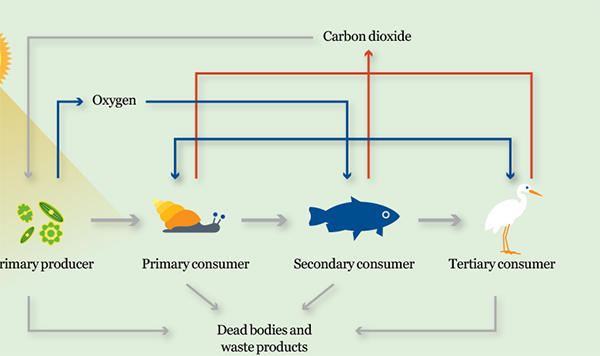
The diagram illustrates the important role that microbes i.e. algae, cyanobacteria and the decomposers, play as primary producers and in the cycling of nutrients.
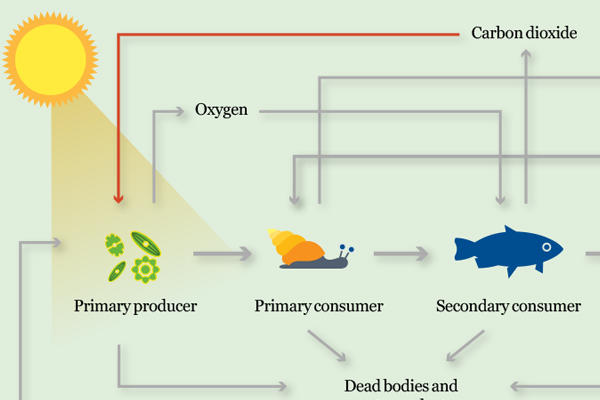
Step 1: Photosynthesis
Step 2: Primary producers
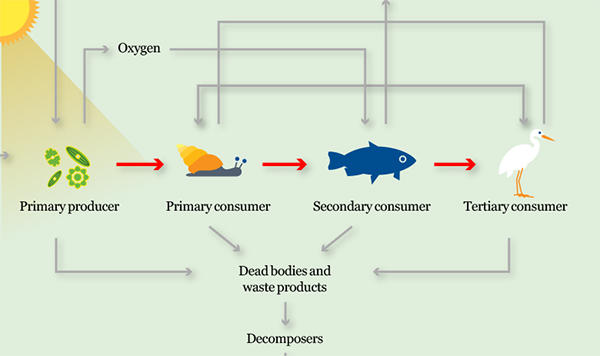
Organisms that make their own food are called primary producers and are always at the start of the food chain.
Animals and micro-organisms like fungi and bacteria get energy and nutrients by eating other plants, animals and microbes.
Step 3: Aerobic respiration
Step 4: Decomposition
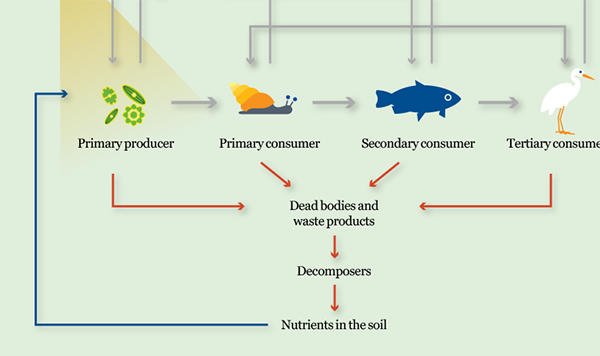
Green algae and cyanobacteria are found at the beginning of the food chain. They are known as primary producers because they make their own food.
-
Carbon cycle
Where has that carbon atom been? The carbon cycle is a complex cyclical process through which all of the carbon atoms in existence rotate.
-
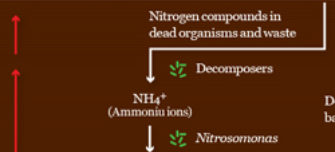
Nitrogen cycle
Similar to the carbon cycle the nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen in all its forms, cycles to the environment.