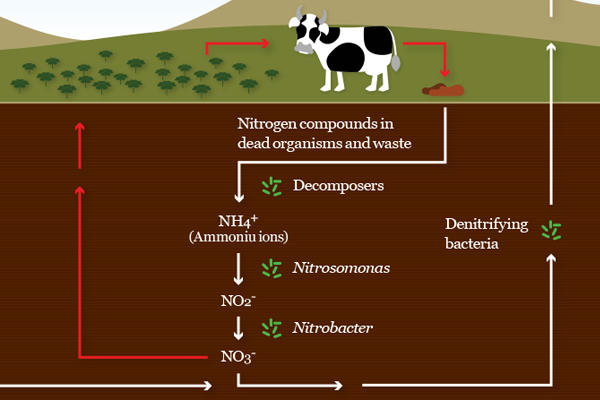
Nitrogen cycle
Plants absorb the nitrate ions by diffusion and active transport. The plants need the nitrogen for the synthesis of proteins and other compounds. The nitrogen compounds are passed through the food chain as other organisms feed on the plants and each other.
Waste products (undigested food, urine and faeces) and dead organisms which contain nitrogen compounds are added to the soil.
Ammonification (decay)
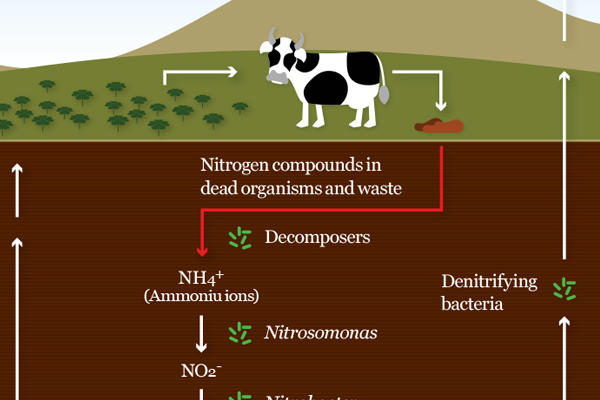
Nitrification
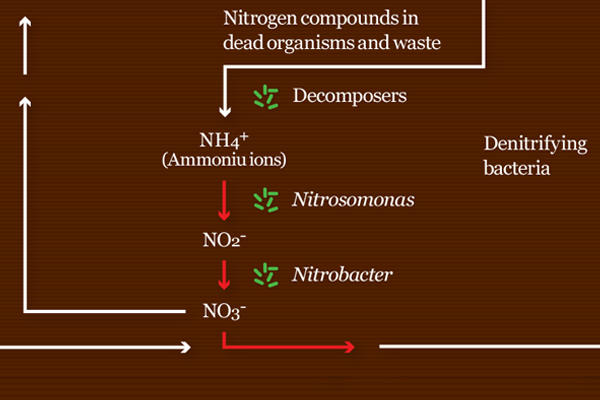
Denitrification
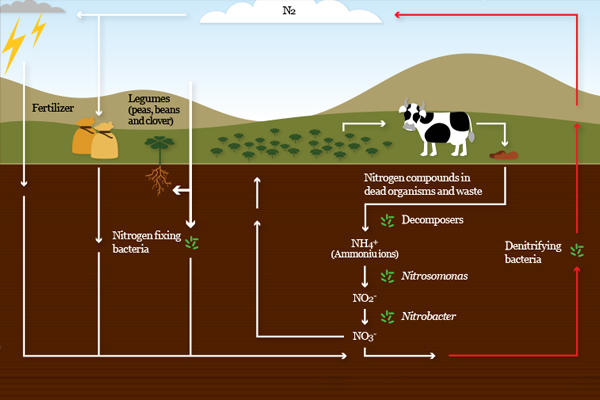
Nitrogen fixation
- Atmospheric fixation - this occurs spontaneously due to lightning. Only a small amount is fixed this way.
- Industrial fixation - the Haber process is used to make nitrogen fertilizers. This is very energy inefficient.
Biological fixation
Nitrogen fixing bacteria fix 60% of nitrogen gas.
- Some nitrogen fixing bacteria e.g. Rhizobium live in the root nodules of legumes.
- Some nitrogen fixing bacteria e.g. Azotobacter are free living in the soil.
Nitrogen in the air
Nitrogen is required by all living organisms for the synthesis of proteins, nucleic acids and other nitrogen containing compounds. The Earth’s atmosphere contains almost 80 % nitrogen gas. It cannot be used in this form by most living organisms until it has been fixed, that is reduced (combined with hydrogen), to ammonia.
The nitrogen cycle is a series of processes that convert nitrogen gas to organic substances and back to nitrogen in nature. It is a continuous cycle that is maintained by the decomposers and nitrogen bacteria. The nitrogen cycle can be broken down into four types of reaction and micro-organisms play roles in all of these.
-
Carbon cycle
Where has that carbon atom been? The carbon cycle is a complex cyclical process through which all of the carbon atoms in existence rotate.
-
Food chain
All living things depend on each other to live. Find out where microbes are in the food chain.